A comprehensive guide to strategic AI governance
As AI technologies reshape industries, the need for structured, principled, and effective governance has never been more urgent. Policymakers and organizations alike are facing increasing scrutiny around transparency, accountability, and ethical deployment of artificial intelligence. In this fast-moving landscape, two major AI governance frameworks have emerged as global touchstones: ISO/IEC 42001 and the NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF).
This resource offers a detailed comparison of ISO 42001 vs NIST AI RMF, helping decision-makers determine which framework best supports their goals or how to combine both to maximum effect.
Understanding the foundations
What is ISO/IEC 42001?
ISO/IEC 42001:2023 is the world’s first international management system standard for artificial intelligence. Developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), it sets out requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Artificial Intelligence Management System (AIMS).
Unlike sector-specific ethical guidelines or narrow technical controls, ISO 42001 provides an organization-wide framework for AI governance that integrates with existing ISO management systems, e.g., ISO 27001 for information security or ISO 9001 for quality.
Key principles embedded in ISO 42001 include:
- Human-centric and trustworthy AI principles
- Lifecycle-based risk management from data acquisition to model retirement
- Transparency and accountability mechanisms
- Stakeholder engagement, both internal and external
- Continuous improvement through incident response and nonconformity management
Organizations can undergo independent audits and obtain certification, signaling their commitment to safe and responsible AI use.
ISO 42001 adopts the High-Level Structure, which is a standardized structure adopted by ISO for all new and revised management system standards. It ensures consistency, compatibility, and easier integration between standards and maps to the concept of the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle:
What is the NIST AI Risk Management Framework?
The NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF), developed by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology and launched in January 2023, is a non-prescriptive, voluntary guidance document designed to help organizations identify, assess, manage, and govern AI-related risks.
Rather than functioning as a compliance standard, the AI RMF is designed to:
- Promote the development of trustworthy AI systems
- Support innovation while reducing harm
- Provide a common language across stakeholders: developers, risk officers, legal teams, and policymakers
It is structured around four interrelated functions:
- Map: Understand the AI context, systems, and stakeholders
- Measure: Assess risks, impacts, and system trustworthiness
- Manage: Prioritize and respond to risks within context
- Govern: Establish overarching policies, processes, and accountability
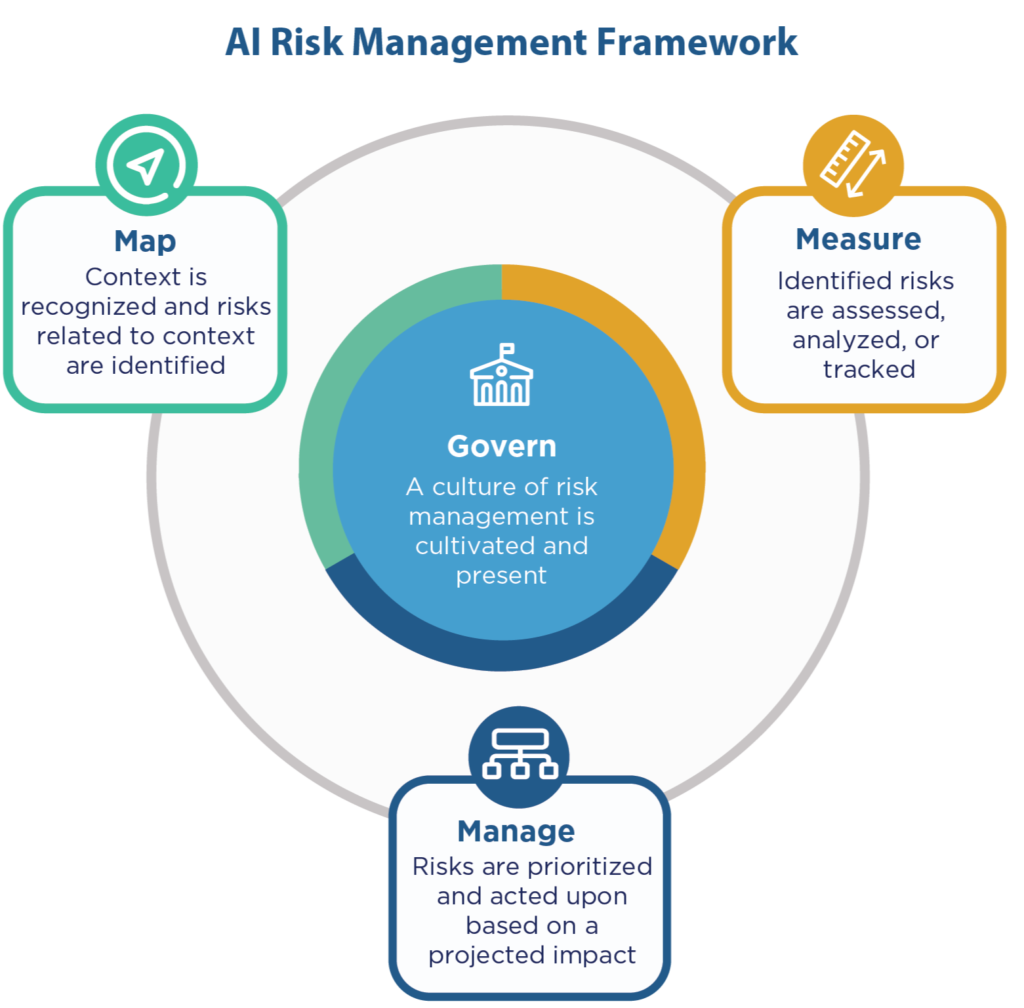
Image courtesy: NIST.
NIST also released an AI RMF Playbook and Profiles, which offer sector-specific adaptations of the framework.
Key areas of comparison
| Category | ISO/IEC 42001 | NIST AI RMF |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Management system standard | Risk management framework |
| Certification | Yes (third-party certifiable) | No (voluntary guidance) |
| Scope | Organizational processes, governance structures, lifecycle oversight | Risk identification, measurement, mitigation, stakeholder communication |
| Origin | International standard (ISO/IEC) | U.S. federal agency (NIST) |
| Regulatory influence | Aligned with global regulatory expectations like the EU AI Act and OECD AI Principles | Influential in U.S. policy and industry self-regulation |
| Stakeholder orientation | Internal and external governance; organizational maturity | Inclusive of developers, users, auditors, civil society |
| Integration with other frameworks | High-Level Structure (HLS) aligns with ISO 27001, ISO 9001, ISO 14001 | Integrates with NIST CSF, Privacy Framework, and emerging AI profiles |
| Level of prescriptiveness | Prescriptive and process-driven | Principles-based and adaptable |
| Lifecycle orientation | Explicitly lifecycle-focused from design to decommissioning | Risk-focused at any stage; adaptable to system maturity |
ISO 42001 and the EU AI Act: towards harmonized standards
A critical development for European organizations, and any company operating in the EU, is the link between ISO/IEC 42001 and the forthcoming harmonized standards under the EU AI Act (see also our EU AI Act Key Takeaways resource).
ISO 42001’s role in European standardization
The European Commission has tasked CEN (European Committee for Standardization) and CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization) with developing harmonized standards to support compliance with the AI Act. These standards will serve as technical benchmarks for fulfilling legal obligations under the Act, especially for high-risk AI systems.
Given its comprehensive, lifecycle-based, and certifiable structure, ISO/IEC 42001 is expected to serve as a core reference, if not the direct basis, for one or more of these harmonized standards. Specifically, it aligns well with the AI Act’s requirements around:
- Risk management systems
- Quality control mechanisms
- Data governance and transparency
- Human oversight and documentation
- Post-market monitoring and incident handling
It is anticipated that ISO 42001, potentially under an “EN ISO/IEC 42001” designation, will be formally referenced in the Official Journal of the EU, granting it the status of presumption of conformity, a powerful legal mechanism under EU product legislation.
Strategic implications
- Adopting ISO 42001 now offers a significant head start in preparing for legal compliance under the AI Act.
- Organizations certified to ISO 42001 will be well positioned to meet conformity assessment requirements under the Act, including when working with notified bodies.
- For developers of high-risk AI systems, ISO 42001 provides a structured path to compliance that’s both internationally recognized and aligned with European regulatory expectations.
Complementarity: not either/or but both
Organizations do not need to choose between ISO 42001 and the NIST AI RMF. In fact, many will benefit by using both strategically and sequentially.
- NIST AI RMF serves as an excellent starting point, especially for organizations at early stages of AI adoption or those operating in agile environments. It helps teams build shared language around AI risks and supports experimental governance initiatives.
- ISO 42001 offers a certifiable governance framework, ideal for organizations looking to institutionalize responsible AI practices and demonstrate compliance to regulators, investors, or customers.
Using the NIST RMF to map and evaluate risk, and ISO 42001 to codify policy, roles, and controls, creates a powerful combination of operational agility and structural assurance with a clear path toward EU regulatory alignment.
Strategic takeaways
Whether you’re a risk manager, C-suite executive, compliance officer, or technical lead, the choice between ISO 42001 and NIST AI RMF is ultimately about strategic alignment with your organization’s:
- Regulatory exposure
- Operational maturity
- Public trust goals
- AI system complexity
At The Governors, we recommend the following pathway:
- Start with elements from NIST AI RMF to assess current state, engage stakeholders, and define risk appetite.
- Use findings to scope an AI governance roadmap aligned with ISO 42001 principles.
- Implement ISO 42001 to embed continuous oversight, risk management, and improvement.
- Prepare for EU AI Act conformity by aligning with future harmonized standards, with ISO 42001 as your base.
Or we work out a tailored roadmap through our AI Governance Roadmap workshop series.
Let’s explore how ISO 42001 and
NIST AI RMF can serve your strategy
Contact us to make AI governance your competitive advantage.